- ExecuteReader : Use for accessing data. It provides a forward-only, read-only, connected recordset.
- ExecuteNonQuery : Use for data manipulation, such as Insert, Update, Delete.
- ExecuteScalar : Use for retriving 1 row 1 col. value., i.e. Single value. eg: for retriving aggregate function. It is faster than other ways of retriving a single value from DB.
Friday, 30 December 2011
What is difference between ExecuteReader, ExecuteNonQuery and ExecuteScalar.
13:38
No comments
Concept of Interface
13:36
No comments
What is Interface?
- An Interface is a group of constants and method declaration.
- .Net supports multiple inheritance through Interface.
- Interface states “what” to do, rather than “how” to do.
- An interface defines only the members that will be made available by an implementing object. The definition of the interface states nothing about the implementation of the members, only the parameters they take and the types of values they will return. Implementation of an interface is left entirely to the implementing class. It is possible, therefore, for different objects to provide dramatically different implementations of the same members.
- Example1, the Car object might implement the IDrivable interface (by convention, interfaces usually begin with I), which specifies the GoForward, GoBackward, and Halt methods. Other classes, such as Truck, Aircraft, Train or Boat might implement this interface and thus are able to interact with the Driver object. The Driver object is unaware of which interface implementation it is interacting with; it is only aware of the interface itself.
- Example2, an interface named IShape, which defines a single method CalculateArea. A Circle class implementing this interface will calculate its area differently than a Square class implementing the same interface. However, an object that needs to interact with an IShape can call the CalculateArea method in either a Circle or a Square and obtain a valid result.
- Practical Example
{
void GoForward(int Speed);
}
public class Truck : IDrivable
{
public void GoForward(int Speed)
{
// Implementation omitted
}
}
public class Aircraft : IDrivable
{
public void GoForward(int Speed)
{
// Implementation omitted
}
}
public class Train : IDrivable
{
public void GoForward(int Speed)
{
// Implementation omitted
}
}
Extra
- Each variable declared in interface must be assigned a constant value.
- Every interface variable is implicitly public, static and final.
- Every interface method is implicitly public and abstract.
- Interfaces are allowed to extends other interfaces, but sub interface cannot define the methods declared in the super interface, as sub interface is still interface and not class.
- If a class that implements an interface does not implements all the methods of the interface, then the class becomes an abstract class and cannot be instantiated.
- Both classes and structures can implement interfaces, including multiple interfaces.
OOPs Interview Questions
13:36
No comments
OOPs FAQs : Object Oriented Interview Questions
Can you prevent your class from being inherited by another class?Yes. The keyword “sealed” will prevent the class from being inherited.
Class
A user-defined data structure that groups properties and methods. Class doesn’t occupies memory.
Object
Instance of Class is called object. An object is created in memory using keyword “new”.
Difference between Struct and Class
- Struct are Value type and are stored on stack, while Class are Reference type and are stored on heap.
- Struct “do not support” inheritance, while class supports inheritance. However struct can implements interface.
- Struct should be used when you want to use a small data structure, while Class is better choice for complex data structure.
What is the difference between instantiating structures with and without using the new keyword?
When a structure is instantiated using the new keyword, a constructor (no-argument or custom, if provided) is called which initializes the fields in the structure. When a structure is instantiated without using the new keyword, no constructor is called. Hence, one has to explicitly initialize all the fields of the structure before using it when instantiated without the new keyword.
When a structure is instantiated using the new keyword, a constructor (no-argument or custom, if provided) is called which initializes the fields in the structure. When a structure is instantiated without using the new keyword, no constructor is called. Hence, one has to explicitly initialize all the fields of the structure before using it when instantiated without the new keyword.
Encapsulation
Wrapping up of data and function into a single unit is known as Encapsulation.
Properties
Attribute of object is called properties. Eg1:- A car has color as property.
Eg2:
private string m_Color;;
public string Color
{
get
get
{
return m_Color;
}
set
{
m_Color = value;
}
}
Car Maruti = new Car();
Maruti.Color= “White”;
Console.Write(Maruti.Color);
Isn't it better to make a field public than providing its property with both set { } and get { } block? After all the property will allow the user to both read and modify the field so why not use public field instead? Motivate your answer
Not always! Properties are not just to provide access to the fields; rather, they are supposed to provide controlled access to the fields of our class. As the state of the class depends upon the values of its fields, using properties we can assure that no invalid (or unacceptable) value is assigned to the fields.Eg:private int age;
public int Age
{
get
{
return age;
}
set
{
if(value <> 100)
//throw exception
else
age = value;
}
}
this Keyword
Each object has a reference “this” which points to itself.
Two uses of this keyword.
o Can be used to refer to the current object.
o It can also be used by one constructor to explicitly invoke another constructor of the same class.
Eg1:
class Student
{
private string name;
private int age;
Student(string name, int age)
{
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
Eg2:
class Circle
{
double x,y,radius;
Circle(double x){
this(x,0,1);
}
Circle(double x, double y){
this(x,y,1);
}
Circle(double x, double y, double radius){
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.radius = radius;
}
}
Constructor
- A constructor is a special method whose task is to initialize the object of its class.
- It is special because its name is the same as the class name.
- They do not have return types, not even void and therefore they cannot return values.
- They cannot be inherited, though a derived class can call the base class constructor.
- Constructor is invoked whenever an object of its associated class is created.
- Note: There is always atleast one constructor in every class. If you do not write a constructor, C# automatically provides one for you, this is called default constructor. Eg: class A, default constructor is A().
Static Members of the class
Static members belong to the whole class rather than to individual object
Static members are accessed with the name of class rather than reference to objects.
Eg:
class Test
{
public int rollNo;
public int mathsMarks;
public static int totalMathMarks;
}
class TestDemo
{
public static void main()
{
Test stud1 = new Test();
stud1.rollNo = 1;
stud1.mathsMarks = 40;
stud2.rollNo = 2;
stud2.mathsMarks = 43;
Test.totalMathsMarks = stud1.mathsMarks + stud2.mathsMarks;
}
}
Static Method of the class
Methods that you can call directly without first creating an instance of a class. Eg: Main() Method, Console.WriteLine()
You can use static fields, methods, properties and even constructors which will be called before any instance of the class is created.
As static methods may be called without any reference to object, you can not use instance members inside static methods or properties, while you may call a static member from a non-static context. The reason for being able to call static members from non-static context is that static members belong to the class and are present irrespective of the existence of even a single object.
Static Constructor
In C# it is possible to write a static no-parameter constructor for a class. Such a class is executed once, when first object of class is created.
One reason for writing a static constructor would be if your class has some static fields or properties that need to be initialized from an external source before the class is first used.
Eg:
Class MyClass
{
static MyClass()
{
//Initialization Code for static fields and properties.
}
}
Finalize() Method of Object classEach class in C# is automatically (implicitly) inherited from the Object class which contains a method Finalize(). This method is guaranteed to be called when your object is garbage collected (removed from memory). You can override this method and put here code for freeing resources that you reserved when using the object.
For example
Protected override void Finalize()
{
try
{
Console.WriteLine(“Destructing Object….”);
//put some code here.
}
finally
{
base.Finalize();
}
}
Destructor
A destructor is just opposite to constructor.
It has same as the class name, but with prefix ~ (tilde).
They do not have return types, not even void and therefore they cannot return values.
destructor is invoked whenever an object is about to be garbage collected
Eg:
class person
{
//constructor
person()
{
}
//destructor
~person()
{
//put resource freeing code here.
}
}
What is the difference between the destructor and the Finalize() method? When does the Finalize() method get called?
Finalize() corresponds to the .Net Framework and is part of the System.Object class. Destructors are C#'s implementation of the Finalize() method. The functionality of both Finalize() and the destructor is the same, i.e., they contain code for freeing the resources when the object is about to be garbage collected. In C#, destructors are converted to the Finalize() method when the program is compiled. The Finalize() method is called by the .Net Runtime and we can not predict when it will be called. It is guaranteed to be called when there is no reference pointing to the object and the object is about to be garbage collected.
Finalize() corresponds to the .Net Framework and is part of the System.Object class. Destructors are C#'s implementation of the Finalize() method. The functionality of both Finalize() and the destructor is the same, i.e., they contain code for freeing the resources when the object is about to be garbage collected. In C#, destructors are converted to the Finalize() method when the program is compiled. The Finalize() method is called by the .Net Runtime and we can not predict when it will be called. It is guaranteed to be called when there is no reference pointing to the object and the object is about to be garbage collected.
Garbage Collection
- Garbage collection is the mechanism that reclaims the memory resources of an object when it is no longer referenced by a variable.
- .Net Runtime performs automatically performs garbage collection, however you can force the garbage collection to run at a certain point in your code by calling System.GC.Collect().
- Advantage of Garbage collection : It prevents programming error that could otherwise occur by incorrectly deleting or failing to delete objects.
Enumeration
Enumeration improves code readability. It also helps in avoiding typing mistake.
Concept of Heap and Stack
| Local Variables | Stack |
| Free Memory (Larger Memory Area than Stack). | Heap |
| Global Variables | Permanent Storage area |
| Program Instruction |
The Program Instruction and Global and Static variables are stored in a region known as permanent storage area and the local variables are stored in another area called stack. The memory space located between these two regions is available for dynamic memory allocation during execution of program. This free memory region is called heap. The size of heap keeps on changing when program is executed due to creation and death of variables that are local to functions and blocks. Therefore, it is possible to encounter memory “overflow” during dynamic allocation process.
Value Type and Reference Type
A variable is value type or reference type is solely determined by its data type.
Eg: int, float, char, decimal, bool, decimal, struct, etc are value types, while object type such as class, String, Array, etc are reference type.
Value Type
As name suggest Value Type stores “value” directly.
For eg:
//I and J are both of type int
I = 20;
J = I;
int is a value type, which means that the above statements will results in two locations in memory.
For each instance of value type separate memory is allocated.
Stored in a Stack.
It Provides Quick Access, because of value located on stack.
Reference Type
As name suggest Reference Type stores “reference” to the value.
For eg:
Vector X, Y; //Object is defined. (No memory is allocated.)
X = new Vector(); //Memory is allocated to Object. //(new is responsible for allocating memory.)
X.value = 30; //Initialising value field in a vector class.
Y = X; //Both X and Y points to same memory location. //No memory is created for Y.
Console.writeline(Y.value); //displays 30, as both points to same memory
Y.value = 50;
Console.writeline(X.value); //displays 50.
Note: If a variable is reference it is possible to indicate that it does not refer to any object by setting its value to null;
Reference type are stored on Heap.
It provides comparatively slower access, as value located on heap.
ref keyword
Passing variables by value is the default. However, we can force the value parameter to be passed by reference. Note: variable “must” be initialized before it is passed into a method.
out keyword
out keyword is used for passing a variable for output purpose. It has same concept as ref keyword, but passing a ref parameter needs variable to be initialized while out parameter is passed without initialized.
It is useful when we want to return more than one value from the method.
Note: You must assigned value to out parameter in method body, otherwise the method won’t compiled.
Boxing and Un-Boxing
Boxing: means converting value-type to reference-type.
Eg:
int I = 20;
string s = I.ToSting();
UnBoxing: means converting reference-type to value-type.
Eg:
int I = 20;
string s = I.ToString(); //Box the int
int J = Convert.ToInt32(s); //UnBox it back to an int.
Note: Performance Overheads due to boxing and unboxing as the boxing makes a copy of value type from stack and place it inside an object of type System.Object in the heap.
Inheritance
The process of sub-classing a class to extend its functionality is called Inheritance.
It provides idea of reusability.
Order of Constructor execution in Inheritance
constructors are called in the order from the top to the bottom (parent to child class) in inheritance hierarchy.
Order of Destructor execution in Inheritance
The destructors are called in the reverse order, i.e., from the bottom to the top (child to parent class) in the inheritance hierarchy.
What are Sealed Classes in C#?The sealed modifier is used to prevent derivation from a class. A compile-time error occurs if a sealed class is specified as the base class of another class. (A sealed class cannot also be an abstract class)
Can you prevent your class from being inherited by another class?Yes. The keyword “sealed” will prevent the class from being inherited.
Can you allow a class to be inherited, but prevent the method from being over-ridden?Yes. Just leave the class public and make the method sealed.
Fast Facts of Inheritance
Multiple inheritance of classes is not allowed in C#.
In C# you can implements more than one interface, thus multiple inheritance is achieved through interface.
The Object class defined in the System namespace is implicitly the ultimate base class of all the classes in C# (and the .NET framework)
Structures (struct) in C# does not support inheritance, it can only implements interfaces.
Polymorphism
Polymorphism means same operation may behave differently on different classes.
Eg:
Method Overloading is an example of Compile Time Polymorphism.
Method Overriding is an example of Run Time Polymorphism
Does C#.net supports multiple inheritance?
No. A class can inherit from only one base class, however a class can implements many interface, which servers some of the same purpose without increasing complexity.
How many types of Access Modifiers.
1) Public – Allows the members to be globally accessible.
2) Private – Limits the member’s access to only the containing type.
3) Protected – Limits the member’s access to the containing type and all classes derived from the containing type.
4) Internal – Limits the member’s access to within the current project.
Method Overloading
Method with same name but with different arguments is called method overloading.
Method Overloading forms compile-time polymorphism.
Eg:
class A1
{
void hello()
{ Console.WriteLine(“Hello”); }
void hello(string s)
{ Console.WriteLine(“Hello {0}”,s); }
}
Method Overriding
Method overriding occurs when child class declares a method that has the same type arguments as a method declared by one of its superclass.
Method overriding forms Run-time polymorphism.
Note: By default functions are not virtual in C# and so you need to write “virtual” explicitly. While by default in Java each function are virtual.
Eg1:
Class parent
{
virtual void hello()
{ Console.WriteLine(“Hello from Parent”); }
}
Class child : parent
{
override void hello()
{ Console.WriteLine(“Hello from Child”); }
}
static void main()
{
parent objParent = new child();
objParent.hello();
}
//Output
Hello from Child.
Virtual Method
By declaring base class function as virtual, we allow the function to be overridden in any of derived class.
Eg:
Class parent
{
virtual void hello()
{ Console.WriteLine(“Hello from Parent”); }
}
Class child : parent
{
override void hello()
{ Console.WriteLine(“Hello from Child”); }
}
static void main()
{
parent objParent = new child();
objParent.hello();
}
//Output
Hello from Child.
Monday, 5 December 2011
How to: Bind a ComboBox or ListBox Control to Data
12:42
No comments
- Set the DataSource property to a data source object.
Possible data sources include a BindingSource bound to data,
a data table,
an array,
a data view,
a dataset,
a data view manager,
or any class that implements the IList interface.
- If you are binding to a table,
set the DisplayMember property to the name of a column in the data source.
- or -
If you are binding to an List,
set the display member to a public property of the type in the list.
Saturday, 3 December 2011
How to Create Crystal Reports in .NET
15:03
No comments
Open --> Visual Studio .NET.
select a new Visual Basic .NET Project.
From main menu in Visual Studio
select PROJECT-->Add New Item .
Then Add New Item dialogue will appear and select Crystal Reports from the dialogue box.
Select Report type from Crystal Reports gallery.
click OK.
Then select the appropriate connection to your database.
Here we are going to select OLEDB connection for SQL Server
Select OLE DB (ADO) from Create New Connection .
Select Microsoft OLE DB Provider for SQL Server .
Next screen is the SQL Server authentication screen .
Select your Sql Server name , enter userid , password and select your Database Name .
Click next , Then the screen shows OLE DB Property values , leave it as it is , and click finish.
Then you will get your Server name under OLEDB Connection from there select database name (Crystaldb) and click the tables , then you can see all your tables from your database.
Select all table from the table list to right side list box, because we are creating report from three tables ( OrderMaster, OrderDetails, Product) .
The next step is to make relation between these selected tables.
Here we are connecting the related fields from each table. For that we arrange the tables in visible area in the list (this is not necessary ) and select the field we are going to make relation and drag to the related field of the other table. After made the relation the screen is look like the following picture .
Next step is to select the fields from the tables .
Here we are selecting only Customername , orderdate from ordermastertable , Productname from product table and quantity from order details.
Click the Finish button because now we are not using other functionalities of this wizard. After that you will get the Crystal Reports designer window . You can arrange the fields in the designer window according to your requirement to view the report . For rearranging you can drag the field object in the screen . For editing right click the field object and select Edit Text Object. The following picture shows the sample of designer window after rearrange the field.
Now the designing part is over and the next step is to call the created Crystal Reports in VB.NET through Crystal Reports Viewer control .
Select the default form (Form1.vb) you created in VB.NET and drag a button and CrystalReportViewer control to your form.
Select Form's source code view and put the code on top......
Imports CrystalDecisions.CrystalReports.Engine
Public Class Form1
Private Sub Button1_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object,
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Button1.Click
Dim cryRpt As New ReportDocument
cryRpt.Load("PUT CRYSTAL REPORT PATH HERE\CrystalReport1.rpt")
CrystalReportViewer1.ReportSource = cryRpt
CrystalReportViewer1.Refresh()
End Sub
End ClassHow to Binding Text Boxes to Data source in C#/VB.NET
14:46
No comments
How to bind textboxes to data source using Visual Studio

Select TextBox &
from the properties window
select (Advanced) from DataBindings

From the list of sources select ‘Add Data Source’
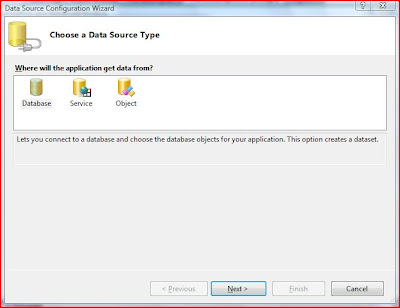
Select Appropriate Data Source

When prompted to Save the connection string accept it

The dialog will get the list of data sources.
From the list select the table you want and the columns
Assign the column to the particular text box
this.textBox1.DataBindings.Add(new System.Windows.Forms.Binding("Text", this.forumUsersBindingSource, "ForumUser", true));
Friday, 2 December 2011
How to Bind a Lisbox to Database in C# (.NET)
12:00
No comments
Bind Listbox to Dataset using Visual Studio
Following steps would help you in connected a database/dataset to the list box
Step1: Add a List Box control to the form and select the DataSource from quick edit
Step 2: Select appropriate data source type (We are going to connect to an SQL Server DB)
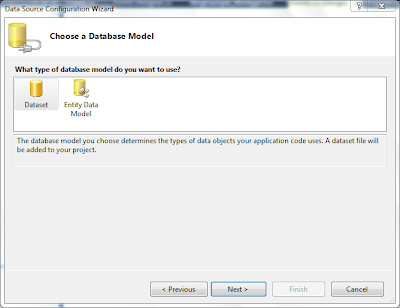
Step 3: Select Appropriate Database Model
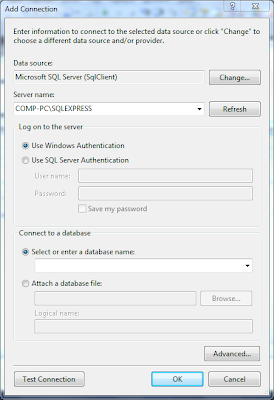
Step 4: Add a connection to database and select appropriate DB
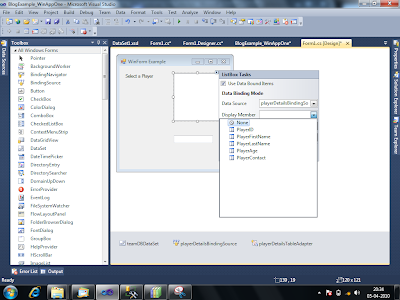
Step 5: Select appropriate field you want to show in listbox
A dataset will be created and will be used for it. You can write necessary code in listbox selectionchange events depending upon the business logic
Following steps would help you in connected a database/dataset to the list box
Step1: Add a List Box control to the form and select the DataSource from quick edit

Step 2: Select appropriate data source type (We are going to connect to an SQL Server DB)

Step 3: Select Appropriate Database Model

Step 4: Add a connection to database and select appropriate DB

Step 5: Select appropriate field you want to show in listbox

A dataset will be created and will be used for it. You can write necessary code in listbox selectionchange events depending upon the business logic
How to send mail using Gmail in C#
11:59
No comments
How to send mail using .NET
Here is a simple code that sends mail from gmail account
I have used this code to get the details from contact page to my mail ID
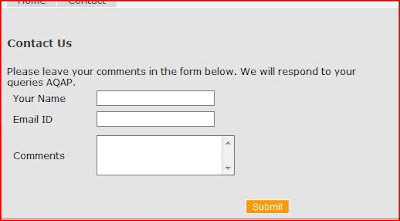
The code uses System.Net Mail namespace
protected void btnSubmit_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
Here is a simple code that sends mail from gmail account
I have used this code to get the details from contact page to my mail ID

The code uses System.Net Mail namespace
protected void btnSubmit_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
try
{
string sFrom = "telanganadeccan@gmail.com";
string sTo = "info@rowsandcolumns.in";
string sMessage = txtComments.Text + "\n" + txtName.Text;
string sSubject = txtName.Text;
string sMail = txtEmail.Text;
MailAddress oMailfrom = new MailAddress(sFrom);
MailAddress oMailTo = new MailAddress( sTo);
MailMessage message = new MailMessage(oMailfrom, oMailTo );
message.Body = "From " + sSubject + "\n Mail ID " + sMail + "\n Comments :\n" + sMessage;
SmtpClient client = new SmtpClient();
client.Timeout = 20000;
message.Subject = sSubject;
client.EnableSsl = true;
client.Send(message );
Response.Redirect ("~/Thanks.aspx");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Response.Redirect("~/Thanks.aspx");
}
}
try
{
string sFrom = "telanganadeccan@gmail.com";
string sTo = "info@rowsandcolumns.in";
string sMessage = txtComments.Text + "\n" + txtName.Text;
string sSubject = txtName.Text;
string sMail = txtEmail.Text;
MailAddress oMailfrom = new MailAddress(sFrom);
MailAddress oMailTo = new MailAddress( sTo);
MailMessage message = new MailMessage(oMailfrom, oMailTo );
message.Body = "From " + sSubject + "\n Mail ID " + sMail + "\n Comments :\n" + sMessage;
SmtpClient client = new SmtpClient();
client.Timeout = 20000;
message.Subject = sSubject;
client.EnableSsl = true;
client.Send(message );
Response.Redirect ("~/Thanks.aspx");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Response.Redirect("~/Thanks.aspx");
}
}
Thursday, 1 December 2011
How to use Treeview designer in C# Application
17:02
No comments
C# Treeview designer example
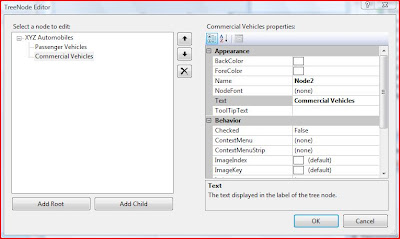
Treeview control gives a nice hierarchical view for the users of a given concept. The following example shows how to create a simple tree-view control using the designer
Add a Tree View Control to the form


Select the TreeView Tasks from the control
Add the root item – XYZ Automobiles
Click the root item and then click on the Add Child to add children. Repeat the steps to add more children
The form will be displayed as shown below

The above can be done through C# code as shown below:
private void AddTreeViewControls()
{
treeView1.Nodes.Add("Root","XYZ Autombiles");
treeView1.Nodes["Root"].Nodes.Add("PV", "Passenger Vehicles");
treeView1.Nodes["Root"].Nodes.Add("CV", "Commercial Vehicles");
}
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)